Material: Carbon Steel (Low Carbon Steel, High Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel)
Measuring System: Metric
Thread Size: M1.6~M52
Length: 2mm~200mm
Surface Treatment: Galvanized
Color: Blue white
International Standard: DIN ANSI BS GB
Thread: Fully-thread
Product Usage: Hexagonal bolts are used in engineering, automotive industry and various construction. The unique shape of the bolt head makes it easy to clamp with a tool from any angle. The blue and white hexagon bolts are more beautiful than the black hexagon bolts, so they are generally used for interior decoration or for fasteners that are presented on the surface.
About the Products:
Hex bolts, consisting of a head and a threaded rod (< male stud) with a nut, are used to fasten two parts with through holes. This way of connecting structural forms is called bolt connection. If the nut is rotated with the bolt, the two parts can be separated, so the bolted connection is a removable connection.
Products Details:
Drawings about DIN EN ISO 4018
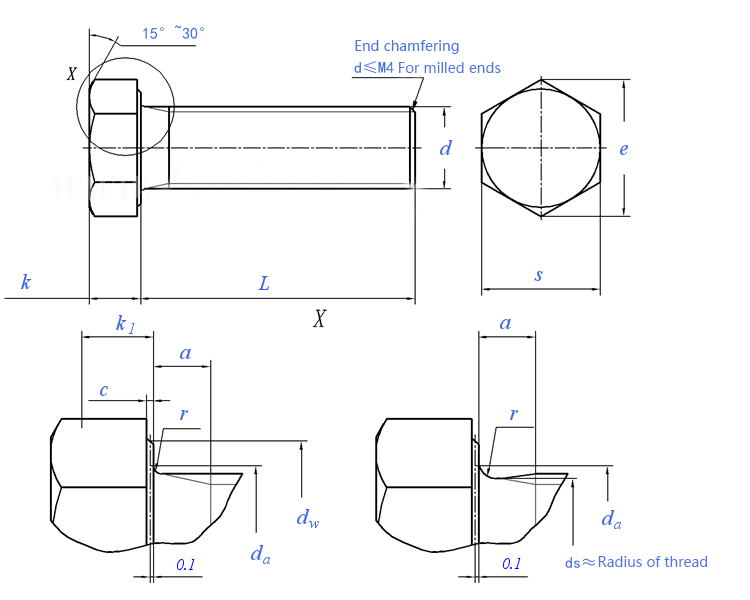
DIN 933 refers to one of the grades of stainless steel hexagon socket screws.
Most of the stainless steel external hexagonal screws are full tooth with hexagonal head full tooth bolts standard: DIN 933, GB 5783, ISO 4017, ANSI B18.2.1, JISB 1180;.
Non-full tooth bolts standard DIN 931, GB 5782, ISO 4014, ANSI B18.2.1, JISB 1180.
Stainless steel hexagonal screws are the most commonly used stainless steel fasteners in the series, and the nuts are used in conjunction with the products with high anti-corrosion requirements and high surface finish requirements, stainless steel hexagonal screws are generally available in full and half tooth, while the half tooth products are divided into coarse rod half tooth and fine rod half tooth.
Additional Information:
The definition of carbon steel is any steel with a carbon content of up to 2.1% of its weight. As the carbon content increases, carbon steel bolts tend to become harder. Although the hardness increases after heat treatment, the ductility of the steel decreases after heat treatment. Regardless of the heat treatment applied to carbon steel alloys, the higher carbon content of the material reduces the weldability of mild steel fasteners and also effectively lowers the bolt's melting point, so most carbon steel bolts are usually relatively weak. As a result they also exhibit low hardness. However, mild steel is highly flexible. High ductility is a property that makes the material well suited for machining and welding. The lack of different elements - used as alloying agents rather than other classes of steel - is the reason why nuts and bolts are called low-cost bolts. Carbon steel nuts and bolts grades are divided into three different categories based on the content of low carbon, medium carbon and high carbon steels.
Introduction About low, medium and high Carbon Steel:
Low carbon steel hexagonal bolts are the most widely used category of all carbon steel groups. Low carbon steel threaded bolts have alloys that typically have a carbon content of less than 0.25% of their total weight. Since this type of carbon steel bolt cannot be hardened by heat treatment to promote martensite formation, the alloy is cold worked.
In this particular category of low carbon steel is another type of steel called High Strength Low Alloy Steel, or HSLA for short. although HSLA bolts belong to a class of low carbon steel, it can be noted that the alloy of HSLA bolts contains other elements such as copper, nickel, vanadium and molybdenum. The combination of said elements adds up to 10% of the weight of the steel content. As the name implies, HSLA bolts have a higher strength, achieved by heat treatment. These washers remain ductile, making them easy to form and machine, while offering higher corrosion resistance than ordinary mild steel.
Medium carbon steel bolts, anchor bolts, threaded rods, studs, nuts and self-drilling screws have a carbon content between 0.25 - 0.60% and a manganese content between 0.60 - 1.65% of their weight. The mechanical properties of these bolts are improved by heat treatment. The heat treatment process involves austenitizing, followed by quenching and tempering. Undergoing these processes is what gives it its martensitic microstructure. Hardened medium carbon steel bolts have greater strength compared to low carbon steel. However, this is a property that comes at the expense of toughness and flexibility.
The carbon content of high carbon steel bolts ranges from 0.60 - 1.25%. High-carbon steel has a manganese alloy content in the range of 0.30 - 0.90 percent. Of all three grades, high-carbon steel threaded rod has the highest hardness and toughness, while exhibiting the lowest ductility. The high wear resistance is demonstrated by the fact that these screws are almost always hardened and tempered.
The two subcategories of tool and die steels, high-carbon steels, contain additional alloying elements such as chromium, molybdenum, vanadium and tungsten. The addition of these minerals results in very hard, strong and wear-resistant hexagonal bolts due to the formation of carbide compounds; for example, tungsten carbide (WC).


Tên đầy đủ: Muxoffer
Hộp thư: info@muxoffer.com
Whatsapp:+86 15507801149
địa chỉ: 3A, Phase II, University Park Lane, Xixiangtang District, Nanning City, Guangxi
